How to apply eczema treatments
Top tips for emollients
- As a moisturiser
Smooth onto clean skin and apply as often as needed to prevent the skin becoming dry. Ideally it should be applied 2-4 times per day.
- As a cleanser
Apply liberally to the skin and wipe off with single layer of paper tissue, taking care not to damage fragile skin.
- As a soap substitute
Mix emollient with water in palm to form lather. Apply to the skin in a downwards direction. Gently rinse lather off skin leaving a thin layer of the ointment on the skin. Pat dry.
- In the bath
Ointments can be dissolved in water. Add a spoon full of ointment to a small amount of hot water in a jug. Then add to the bath water. Take care of the temperature of the water and when getting out of the bath, as it will be slippy.
How should emollients be applied?
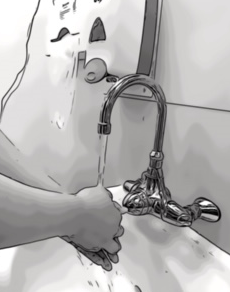
Step 1
Always wash your hands for 20 seconds before applying a topical corticosteroid.

Step 2
Do not put your fingers into the tub as this can introduce bacteria and cause infection. Use a clean spoon or a spatula to take your emollient out of the tub.
If your emollient is in a pump this can be done straight on to your clean hands.
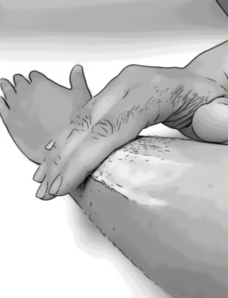
Step 3
Apply to the affected area in a downwards motion following the hair growth.
Do not rub in as this can block the follicles and cause infection.
What are topical corticosteroids?
Topical corticosteroids are a form of medicine applied directly to the skin which helps reduce inflammation, redness and irritation. The type of steroid is similar to those produced naturally in the body.
What are the different strengths of topical steroids?
Your doctor or specialist nurse will identify the correct strength of steroid for different parts of the body and discuss how to increase or decrease treatment appropriately using the steroid ladder.
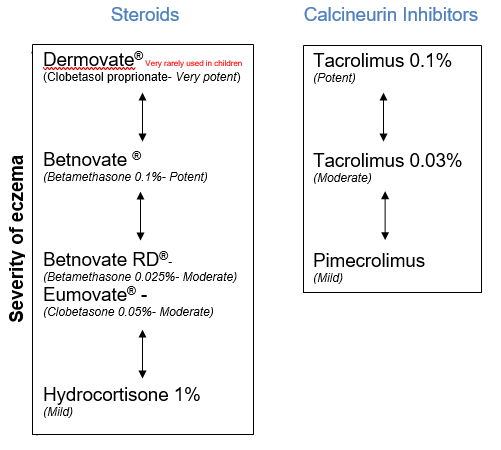
Topical corticosteroids are used on adults, children and young people. More potent steroids are typically in adults used on the affected areas on the body and mild/moderate steroids on the face and skin folds (under arms, breast folds, groin and genitals).
Children and young people will be guided by their doctor or specialist nurse with the use of mild and moderate steroids however when required potent steroids will be used when treating severe skin conditions.
How long should I use topical corticosteroids?
It is important that you follow the treatment plan given by your doctor or specialist nurse in order for your skin to avoid a flare of your skin condition. If used correctly topical corticosteroids should not cause side effects. Thinning of the skin and stretch marks will occur only if a strong steroid is used incorrectly or over a prolonged time.

Step 1
Always wash your hands for 20 seconds before applying a topical corticosteroid.

Step 2
Squeeze the topical steroid in a line from the last finger crease to the fingertip. This is a fingertip unit (FTU).
One FTU would be sufficient to treat an area equivalent to two adult handprints

Step 3
Apply to the affected area in a downwards motion following the hair growth.
Do not rub in as this can block the follicles and cause infection.
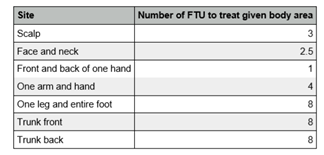
How much topical corticosteroid should be applied?
One (FTU) fingertip unit would be sufficient to treat an area equivalent to two adult handprints. In children the fingertip and two handprints are based on that of an adult also. A thin shiny layer should cover the affected area
The tables below show how much is estimated to be used. This is based on the whole area being treated therefore if only a proportion is affected the amount would be reduced.
Children
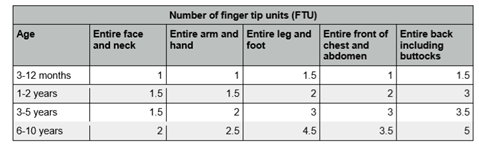
Adults and young people
Precautions
- Topical corticosteroids and emollients contain paraffin which is flammable. Do not smoke, use naked flames (e.g. candles, BBQs, lighters, cigarettes) whilst these products are in contact with your skin, clothes dressings or bandages.
- If a topical corticosteroid causes irritation, please seek advice from your medical or nursing team.
- An emollient should be applied at least 30 minutes after applying a topical steroid or vice versa.
- If you are having ultraviolet light treatment or radiotherapy, check with your medical and nursing team if there is any specific guidance on your emollient use prior to starting treatment.
- Topical corticosteroids and emollients do not contain SPF and should not be used as sun protection. Sun creams should be used when skin is exposed to direct sunlight with a medium/high UV level.
Wet wraps
Wet wrap bandages consist of two layers of medical grade viscose clothing or bandage. The first layer is applied wet and the second dry. Wet wraps help to moisten the skin and reduce irritation. Wet wraps can help intensify topical corticosteroid treatment. As the garment slowly dries out, the skin feels cooler which can help to reduce the itch sensation. Furthermore, they assist in breaking the itch-scratch cycle with eczema due to the barrier it provides in access to direct skin.
Common brands of garments / tubular bandage include Clinifast®, Comfifast®, Skinnies® and Tubifast®. The garments and tubular bandages come in different sizes to suit different aged children and large and small adults.
Paste bandages
Paste bandages are soaked in zinc oxide or zinc oxide plus ichthammol. These ingredients make the bandage soothing and cooling which helps to relive itching and soreness. Paste bandages have anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties.
How do you apply paste bandages?
There is a special way to apply paste bandages because as they dry they can become tighter. Therefore, extra room is needed to make sure they remain comfortable. This technique should be demonstrated to you by a healthcare professional in the department.
Do not apply around the neck, face or torso to avoid suffocation.
Arm Application (National Eczema Society, 2018)
- Wash your hands.
- Open the pack and remove bandage.
- Start at the hand and work up the arm. Wrap the paste bandage around the wrist, smoothing it into place. After each turn, reverse the direction of the winding to form a pleat.
- Continue up the arm and over the elbow, smoothing the paste bandage into place and reversing the direction of the winding (clockwise/anticlockwise) with each turn to make a pleat.
- Secure the paste bandage in place with a dry bandage, such as CLINI fast Tubular Bandage.
- If the fingers are affected, small strips of paste bandage can be wrapped around individual digits and moulded for comfort.
Patch Application
- Wash your hands.
- Open the pack and remove bandage.
- Cut an appropriate size patch and apply directed to the skin.
- Secure in place with dry bandage, such as CLINI fast Tubular Bandage. Alternatively secure in place with Cotton Garments.
Leg Application (National Eczema Society, 2018)
- Wash your hands.
- Open the pack and remove bandage.
- Start at the base of the toes and wrap paste bandage around the ball of the foot or heel, smoothing it into place. After each turn, reverse the direction of the winding to form a pleat.
- Continue up the lower leg and over the knee to the top of the leg, smoothing the paste bandage into place and reversing the direction of the winding (clockwise/anticlockwise) with each turn to make a pleat.
- Secure the paste bandage in place with a dry bandage, such as CLINI fast Tubular Bandage.
- If the toes are affected, small strips of paste bandage can be wrapped around individual digits and moulded for comfort.
What are the possible side effects of paste bandages?
Commonly paste bandages are used with topical corticosteroids underneath which increases the strength of them. A healthcare professional should always discuss your treatment plan with you before using paste bandages and topical corticosteroids together.





